AMOS is a large-scale, clinical and diverse Abdominal Multi-Organ Segmentation benchmark.
News:
-
We associated with MICCAI 2022 to host together MICCAI AMOS Segmentation Challenge 2022 . It’s a registered challenge in MICCAI 2022 and the website has opened. Please visit our chanllenge website for more infomation (Timeline, Instruction etc.) !!!
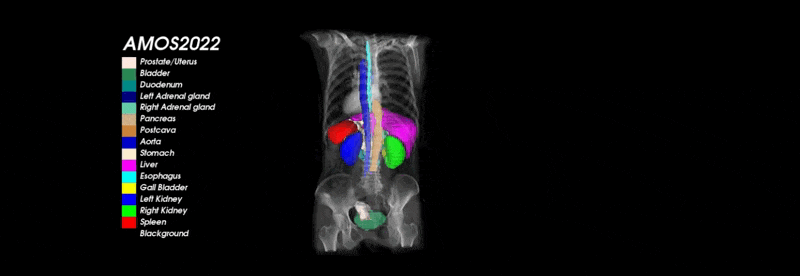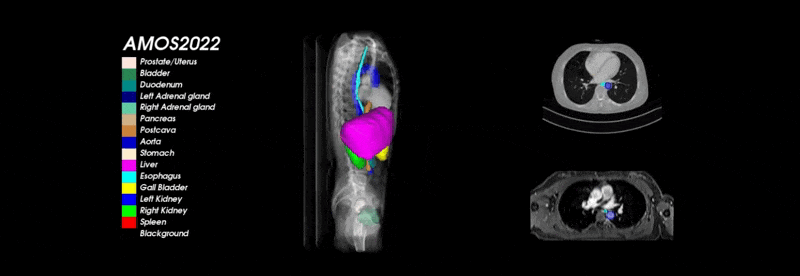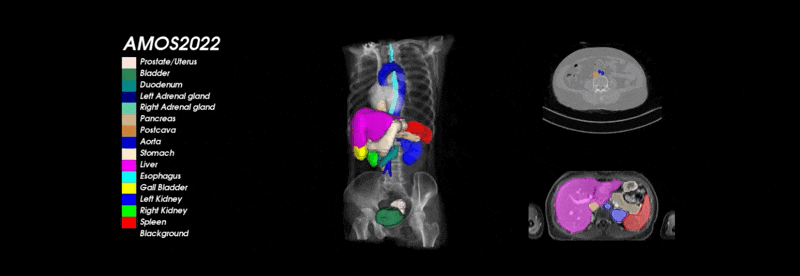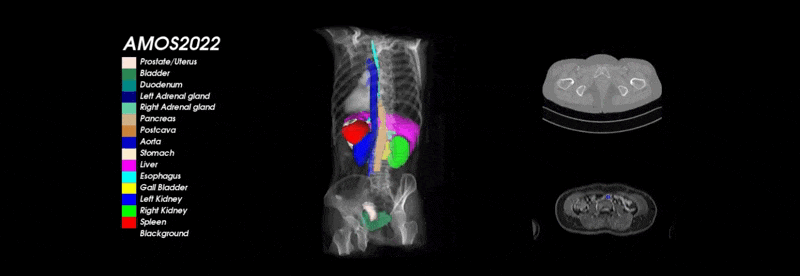
What is and Why AMOS?
Abdominal multi-organ segmentation is one of the most attractive topics in the field of medical image analysis, which plays an important role in supporting clinical workflows such as disease diagnosis and treatment planning.
The recent success of deep learning methods applied for abdominal multi-organ segmentation exposes the lack of large-scale comprehensive benchmarks for developing and comparing such methods. While several benchmark datasets for abdominal organ segmentation are available, the limited number of organs of interest and training samples still limits the power of modern deep models and makes it difficult to provide a fully comprehensive and fair estimate of different methods.
And, most research in medical image analysis today focuses on building bespoke systems to handle stereotypical inputs and outputs associated with a single task, the complexity of systems like this can grow dramatically as the inputs or outputs grow more diverse. If a single algorithm could handle a wide variety of input patterns and outputs, the actual deployment would be greatly simplified, and it would be consistent with human capabilities: the ability to absorb data from many sources, learn common rules, integrate them seamlessly, and serve a variety of tasks.
To address the above drawbacks and further promote the development of medical image segmentation technology, we present AMOS, a large-scale, clinical and diverse abdominal multi-organ segmentation benchmark. It provides 500 CT and 100 MRI scans collected from multi-center, multi-vendor, multi-modality, multi-phase, multi-disease patients, each with voxel-level annotations of 15 abdominal organs.







